What You Need To Know About The Different Product Manager Roles - Part 1
Download the card set and get to know all of the different Product Management roles and flavors.
I always say that Product Management is one of the best examples of versatile jobs out there covering various roles or flavors, such as consumer, enterprise, e-commerce, marketplace, growth, machine learning and many others.
Conveniently, PMs can switch between these roles with their skills driving success with more than one specialized knowledge that can bring big contributions to the companies.
The following article is to answer
question:BTW Justin writes Turtle's Pace. His newsletter is about clear thinking and the creative process with bad doodles that will teach you something useful and will definitely make you laugh!
B2C Product Managers
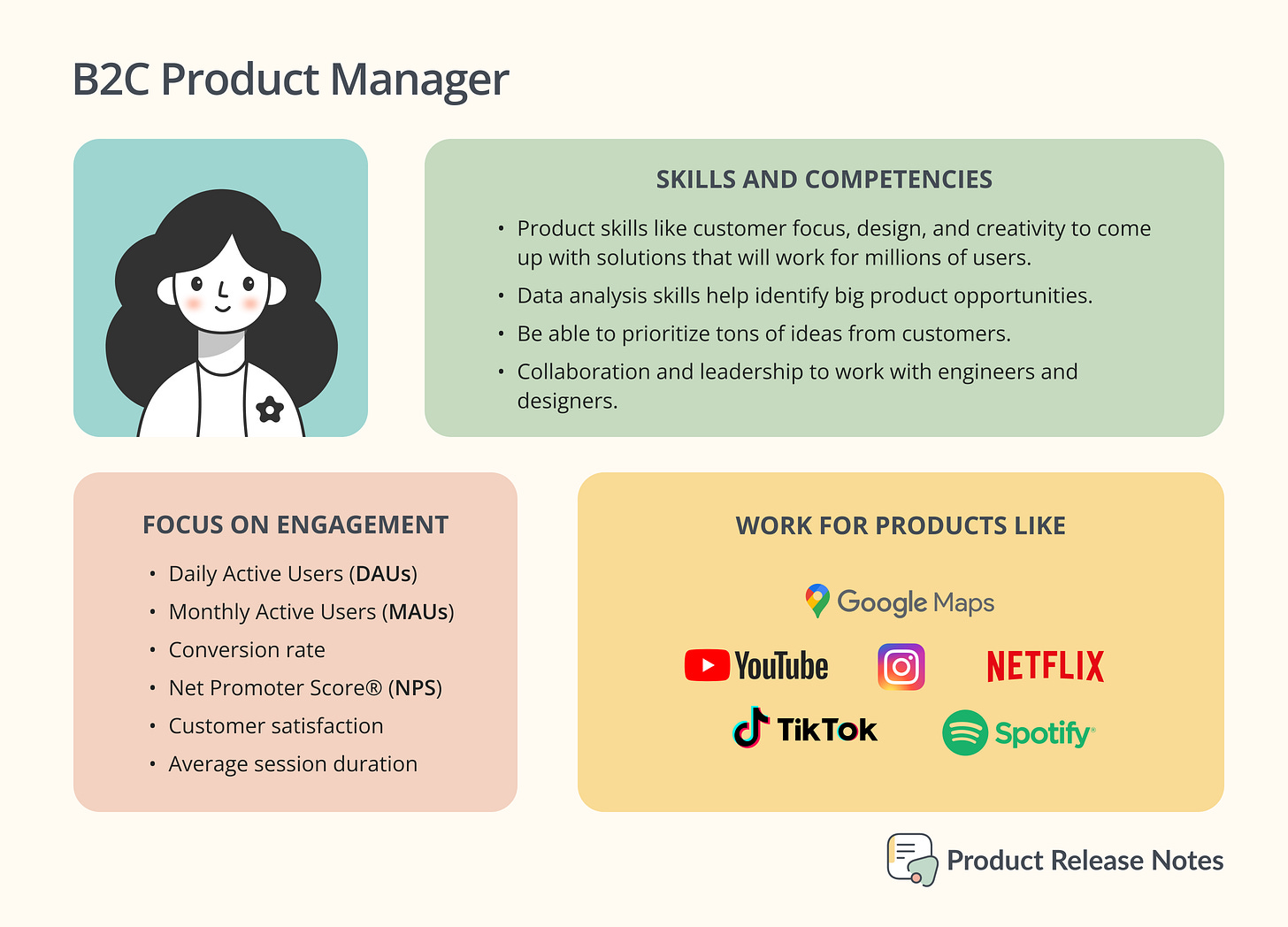
Consumer Product Management roles involve working on user-facing features for products targeting everyday people such as Spotify, Instagram, TikTok, Netflix, etc. They are popular because many PMs like working on products they enjoy.
Focus on
Consumer Product Managers work on user-facing features for products targeting everyday people. They focus on success metrics measuring engagement, such as Daily Active Users (DAUs) or Monthly Active Users (MAUs), to track increasing frequency of use in a growing user base. They might also own usage or transactional metrics for their specific area, such as messages sent or reviews written.
Skills and Competencies
Product skills like customer focus, design, and creativity are crucial for consumer facing Product Managers. They must consider user problems and come up with solutions that will work for millions of users, while being mindful of the needs of the "silent majority" and not just the "vocal minority". Data analysis skills help identify big product opportunities, and prioritization and saying no become important due to the abundance of ideas. Collaboration and leadership skills are also necessary to work with engineers and designers.
B2B Product Manager
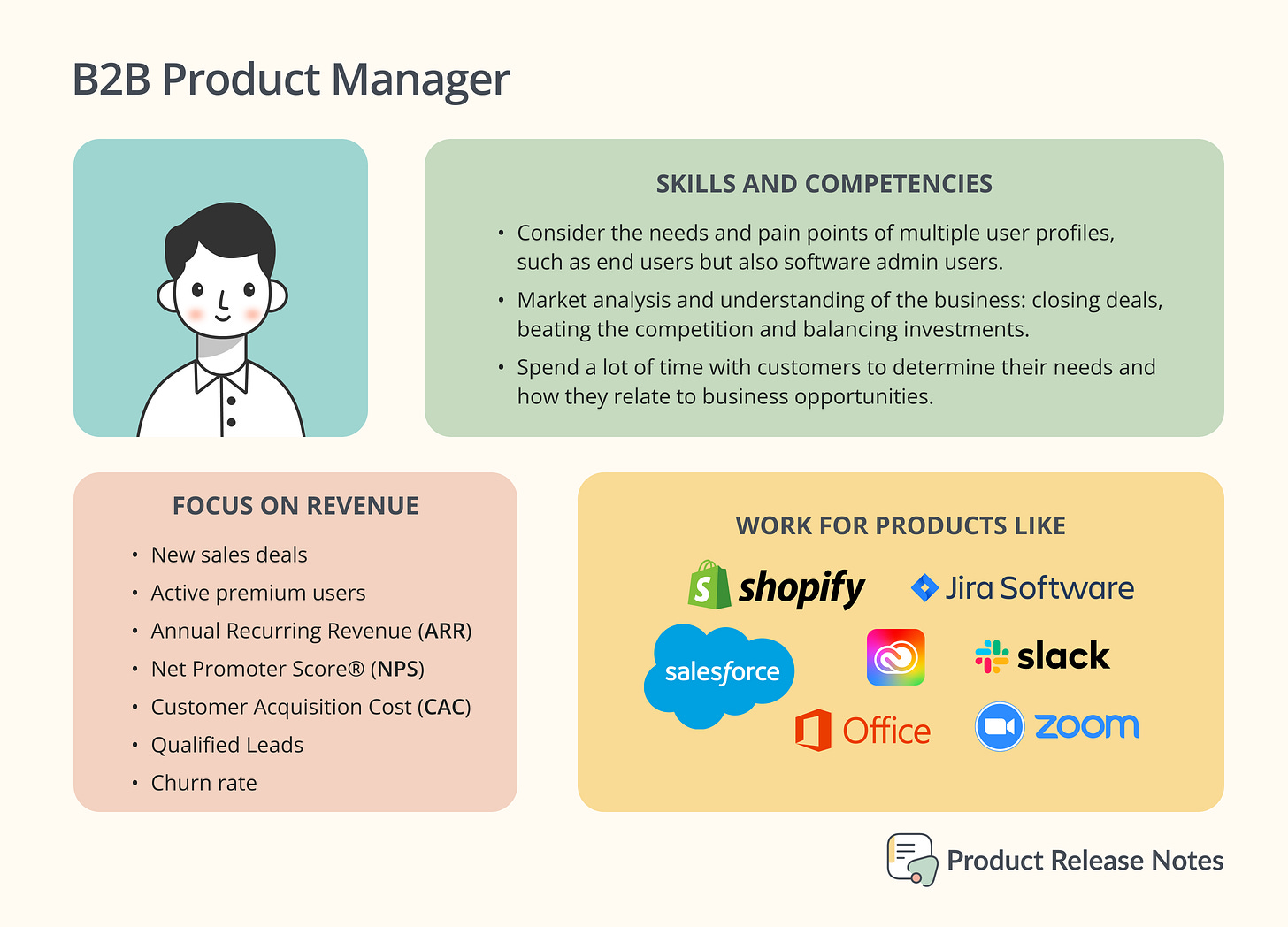
Product Managers working in Business-to-Business often sell solutions to businesses, schools, or even people at work. These B2B products may not have the same name recognition as consumer products but are a great place for PMs to learn in a straightforward way about what customers want and what they find valuable. Some examples of these type of products include Adobe Creative Cloud, Jira, Google Drive, Microsoft Office Suite, Salesforce, Zoom, Slack and Shopify.
Focus on
B2B PMs focus on success metrics that measure revenue, such as new sales deals, annual recurring revenue, and active premium users. They also often focus on engagement with their features. This might be measured by new sales deals the features helped close, like annual recurring revenue (ARR).
Skills and Competencies
B2B Product Managers need to consider the needs of multiple user profiles, from the users that will use the product and the users that will administer the software. A big mistake sometimes PMs do is just focusing on the needs of the buyer/acquirer instead of considering the pain points of the end users and they end up building a product with a miserable experience.
Market analysis and understanding business models are crucial skills for these roles. They also need to focus on closing deals, beating the competition, and balancing investments. Good PMs never ignore monetization opportunities. Also, these PMs spend a lot of time with customers to determine their needs and how they relate to business opportunities.
E-commerce Product Manager
E-commerce companies sell products online and most of the times they deliver them in real life. They utilize supply chain management as a fundamental practice, because delivering fast and efficient is often more important than having a good looking website. Examples of e-commerce companies are Amazon, Alibaba, Apple and Walmart.
Focus on
The main success metric at E-commerce companies is usually successful orders and the conversion funnel leads up to that. An example of a conversion funnel: visiting the site, viewing a product, adding it to the cart, checkout and purchasing. That’s why, it’s important to fulfill orders and deliver them on time to ensure customer satisfaction and loyalty, otherwise clients may never come back.
Skills and Competencies
Execution skills stand out in this area. But dealing with physical goods and financial transactions is never easy, E-commerce is a complex system where mistakes can have severe repercussions to the company. However, good PMs spend some time managing the merchandising and they even answer some support tickets to understand users pain points. They do everything to get the 360-degree view from the customer perspective.
Gaming Product Manager
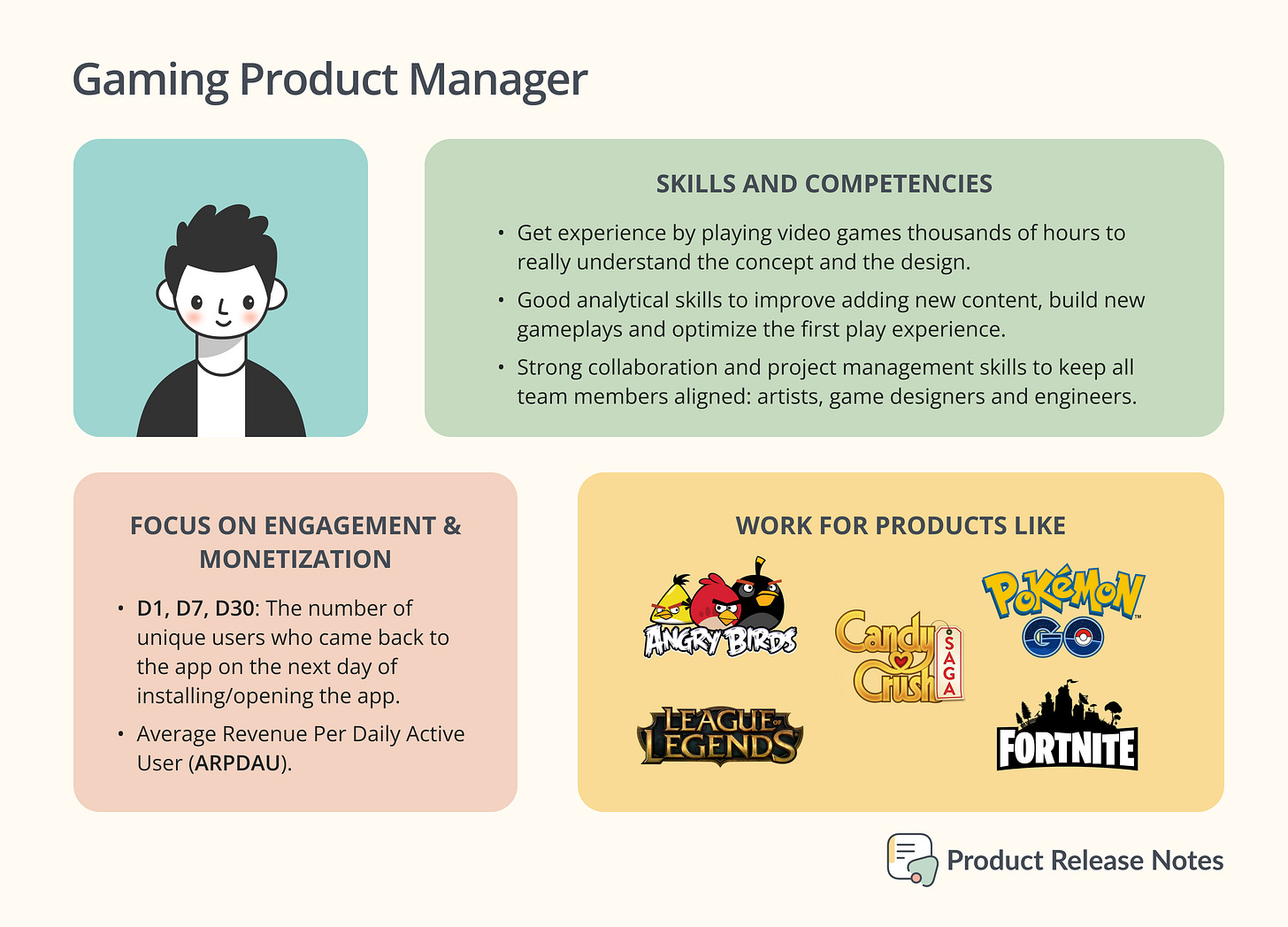
Product Management was not a role related to the game industry, but that was when games used to be only for consoles. Now, even traditional game studios are hiring Product Managers. PMs are becoming increasingly common in the gaming industry, especially for online and mobile games, including popular titles such as Candy Crush, Pokémon Go, Fortnite and League of Legends.
Focus on
PMs at game companies focus on metrics related to player engagement and monetization, such as D1 and D7 retention and ARPDAU. Successful free-to-play games are built with the business model in mind from the beginning. Mobile games primarily acquire new users through ads, so it's important to compare long-term value to CPI.
Also, the type of gameplay determines which monetization strategies will work for the game, such as paying for cosmetic items or more powerful characters. The Product Manager works with the game designer to develop both the core game and the surrounding elements. Commonly, gaming PMs don’t launch new games yet they focus on optimizing and improving a game after its launch during the LiveOps phase, constantly analyzing data and adding new features.
Skills and Competencies
Being a gaming Product Manager requires strong project management skills to keep all team members aligned, including artists, designers, engineers, and more. In addition, having extensive experience playing games is also important to understand different systems and have empathy for players.
In some game companies, the prerequisite for PMs is to play at least 1,000 hours of each game. This is very recommended to gain expertise in game design and functionalities. Being a gaming PM can be a dream job for those who love video games.
Marketplace Product Manager
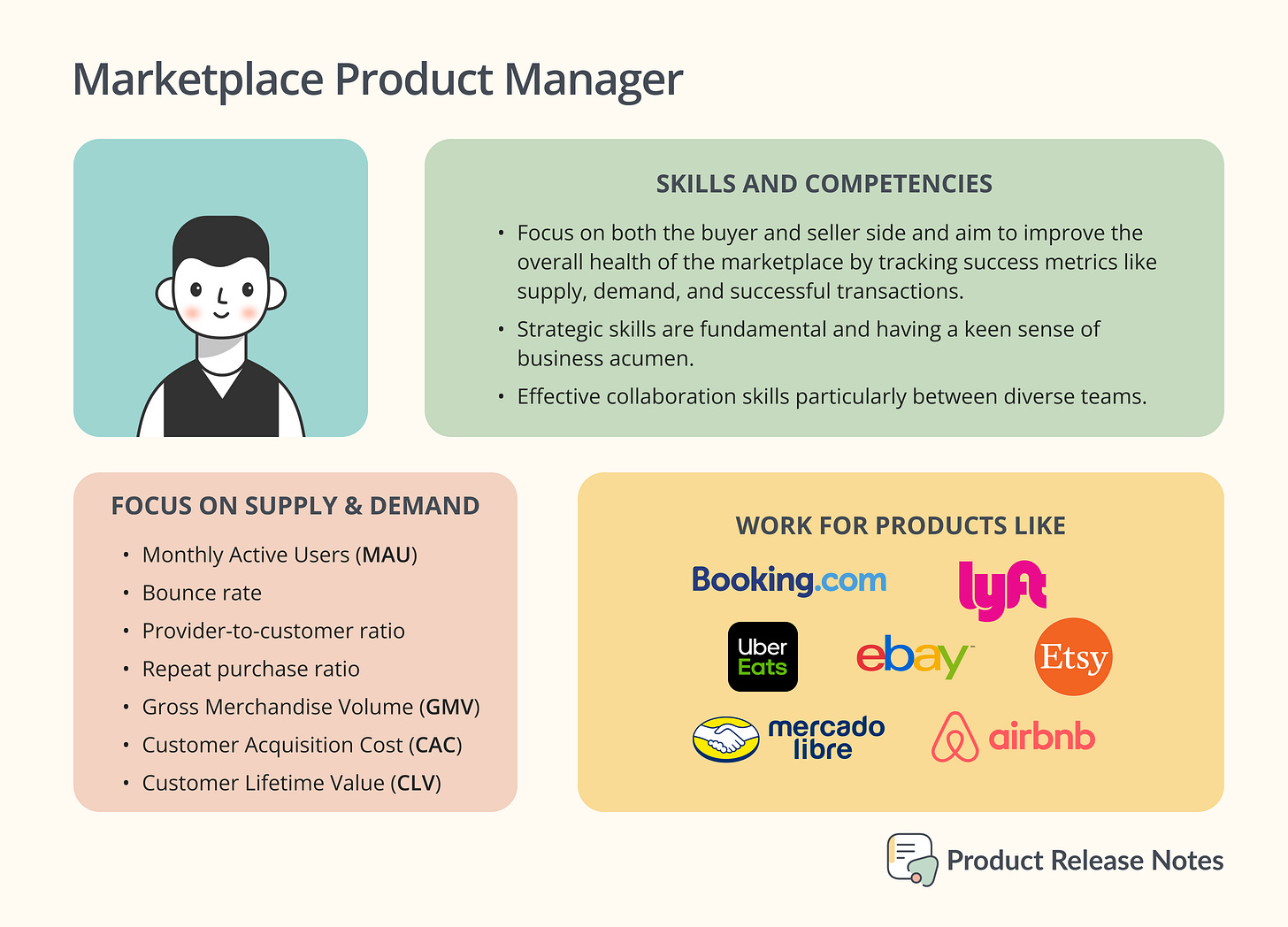
This includes two-sided marketplaces that connects buyers and sellers or service providers with each other. Some examples of these products are Uber, Airbnb, Booking.com, Etsy and Mercado Libre. PM roles on the buyer-side are often consumer or e-commerce roles, while roles on the seller-side are often B2B roles.
Focus on
Marketplace PM roles focus on both the buyer and seller side and aim to improve the overall health of the marketplace by tracking success metrics like supply, demand, and successful transactions. They consider the interplay between supply and demand and work on both sides of the marketplace, meaning from the buyer and the seller side.
Skills and Competencies
Strategic skills are fundamental like a keen sense of business acumen and a effective collaboration skills particularly between diverse teams, are essential for success in these products.
Internal Teams Product Manager
PMs for internal teams create products for other employees within the same company, including infrastructure, sales, data scientists, customer support, and marketing teams. They also create tools to support the main functions of the company.
Focus on
These PMs work closely with other teams, executives, and the company as a whole. Conflicts can arise between the team leaders and internal customers, and it's the PM's job to understand these conflicts, find solutions, and address concerns while implementing solutions. Examples of conflicts include company-wide mandates for product teams and building automation tools that may take away tasks from other teams.
Skills and Competencies
PMs need strong stakeholder management and relationship-building skills to address tensions and prioritize customer focus. They should learn about the needs and fears of internal teams and come up with solutions that address them, even if it includes suggesting new work. Strategic skills are important for internal teams and creating a clear mission can help prioritize work and measure success and get out of firefighting mode.
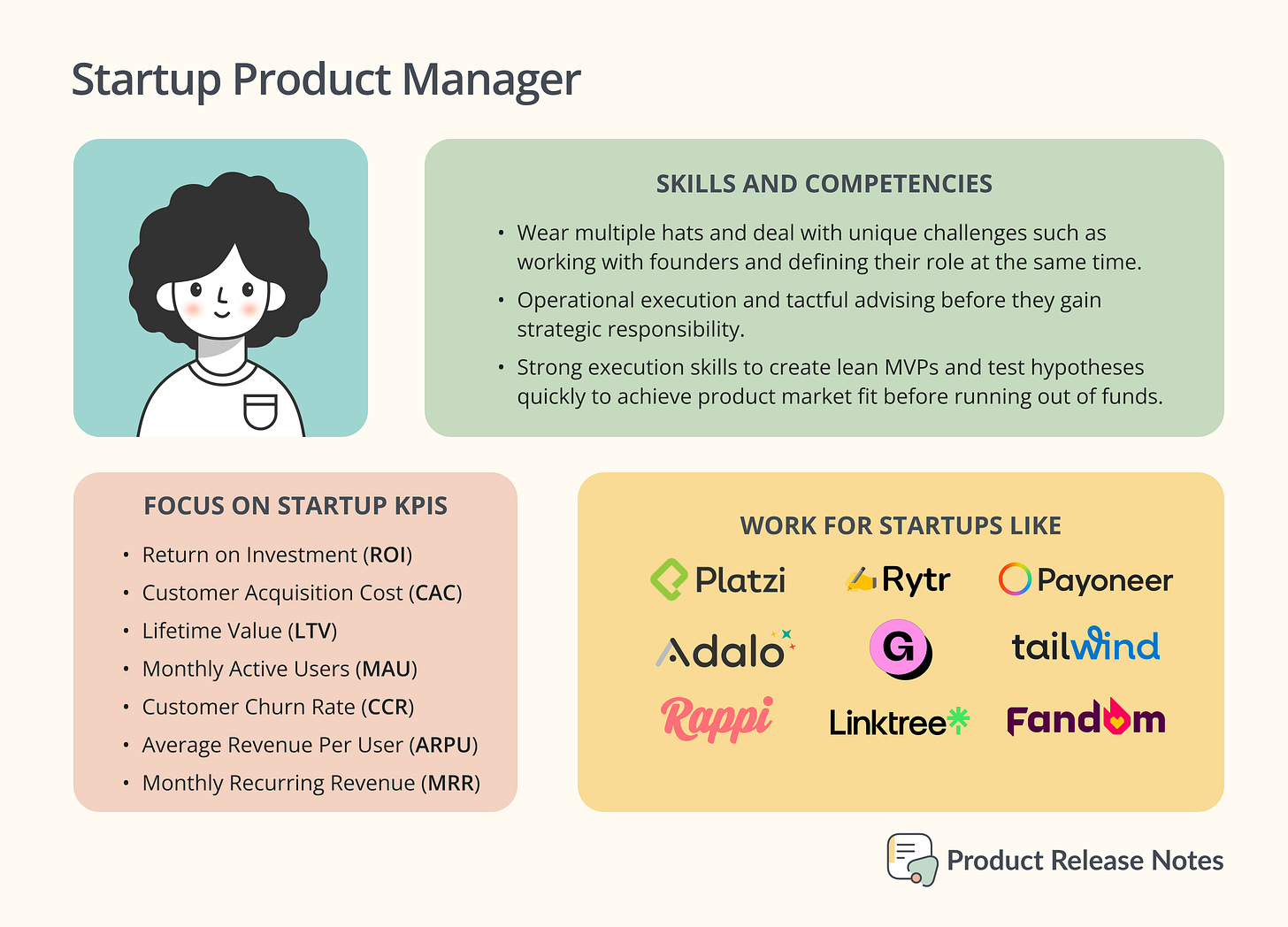
Startups Product Manager
Startups usually have one founder as the first PM, but as the team grows, new PMs may be hired to remove bottlenecks. Joining a fast-growing startup can be beneficial for career growth, but there may not be strong product leaders to learn from. Additionally, if the startup fails, it may be harder to find a new job compared to working at a well-known company.
Focus on
Product Managers at startups have to wear multiple hats and deal with unique challenges such as working with founders and defining their role at the same time.
Early PMs need to prove themselves through operational execution and tactful advising before they gain strategic responsibility. But PMs with a "CEO of the product" mindset can clash with the founder's desire to retain control over the product vision and details.
PMs at startups should ensure they are aligned with the founders and their vision before joining the company. It is essential to clarify expectations and responsibilities, as some founders might want PMs to focus solely on execution or make design-level tweaks to features. They also face challenges in helping the team adapt to having other PMs and showing how they can add value to the process.
Skills and Competencies
PMs at startups need to network outside of their company for advice and mentorship as they often face new tasks with limited resources like recruiting personal, hiring research services, write monthly newsletters, finding co-working spaces, recording tutorials, planning go-to-market campaign and more activities they never have done before.
Also, these PMs need strong execution skills to create lean MVPs and test hypotheses quickly to achieve product market fit before running out of funds.
You can download the whole card set in high resolution PNG and PDF on Gumroad.
Wait for the part 2! Remember, you can drop your questions in the chat (now works on the web).







This is awesome! Thank you for not only answering my question but creating the perfect reference material for anyone seeking to understand this nascent role! I especially love that you called out the "Internal Teams Product Manager"--it seems like more and more businesses are seeing the value of product thinking and creating PM roles for internal systems. The skillset has some unique qualities, as you mention, but all the baseline principles around prioritization, user research, and roadmapping still apply. Thanks again, Elena!
Woow! This is now my go-to-guide for this topic. Thanks for this, Elena!
🤯🤩