Product Management Skills + Checklist Template
Freebie inside with a list of Product Management skills that you can start addressing this year.
Product Management skills may differ between company or organization. Most of the times, the role and activities depends on the size of the company and the type of product or service. While some companies are looking for Product Managers that are more strategic or evangelists, in other places they praise for a more tactical role that focuses on overseeing the day-to-day development of the product.
Of course, this also ends up affecting the type of responsibilities. If two Product Managers from different companies go out for a cup of coffee, they could find out that even if they have the same title, the day-to-day activities may differ slightly or significantly for each one of them.
But relax, there’s a common ground here. Product Managers are well known for their ability to develop different skills. So even if your company organizes the skills differently, you can start addressing skills that are part of the role.
Let’s break down into each one 👇
Execution Skills
Project Management: Project management is the practice of organizing and managing a team’s resources in order to achieve a specific goal or complete a project.
Example: creating a timeline for a project, assigning tasks to team members, and tracking progress.
Scoping and Incremental Development: This skill involves breaking a project down into smaller, more manageable tasks and then working through them incrementally.
Example: defining the scope of a project, creating a plan for progressing through the tasks, and reviewing the progress of each task.
Product Launches: it requires careful planning, organizing, and execution. Product managers need to create compelling product offerings, identify target markets, and develop a launch strategy.
Example: creating a marketing strategy, develop effective promotional campaigns, create pricing structures, setting up a launch event, and tracking the launch’s success.
Get Things Done: This skill involves managing workloads, prioritizing tasks, and taking action to achieve results.
Example: setting goals and deadlines, breaking down larger tasks into smaller ones, and delegating responsibility to team members.
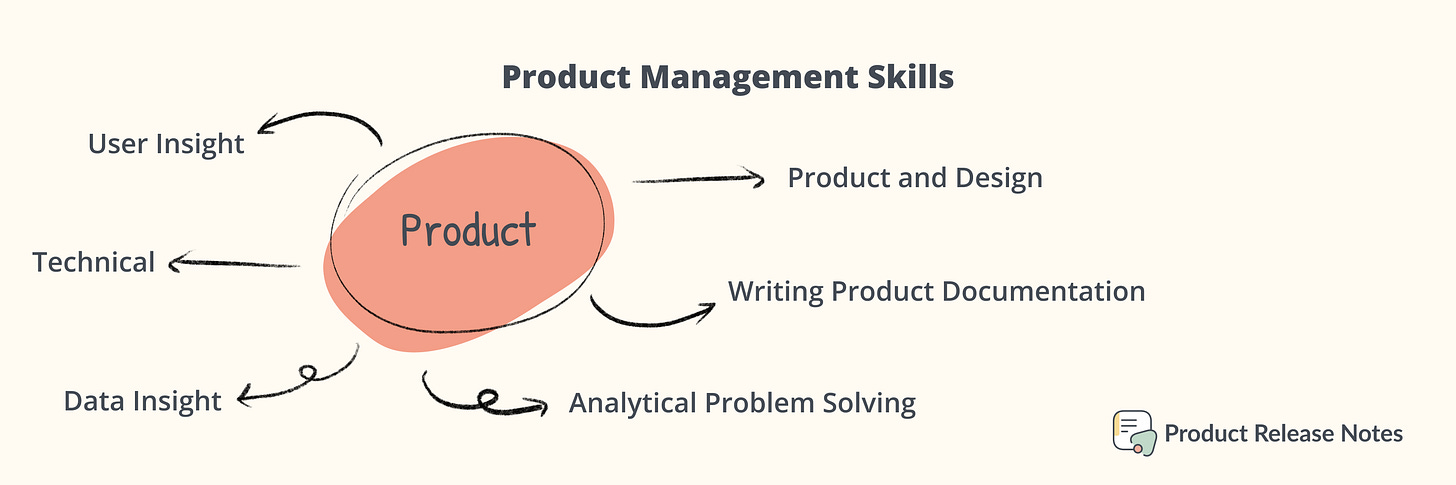
Product Skills
User Insights: This skill involves understanding the needs, preferences, and behaviors of your users. It requires a combination of research-gathering methods, such as interviews, surveys, and analytics, to gain a thorough understanding of your users.
Example: you might conduct interviews with users to understand what features they would like to see in a product, or you might analyze user data to understand the most popular features of a product.
Data Insights: This skill involves analyzing data to uncover trends and insights. It requires the ability to collect, organize and interpret data to help inform product decisions.
Example: you might use data to understand how people are using a product, or to identify areas of the product that are in need of improvement.
Analytical Problem Solving: This skill involves analyzing problems and developing solutions. It requires the ability to break down complex problems into individual components and identify solutions that are practical and effective.
Example: you might analyze user feedback to identify common issues with a product, or develop a plan to address a product-related problem.
Technical Skills: This skill involves understanding the technology behind a product. It requires the ability to work with software, hardware, and other technologies to ensure the product is functioning appropriately.
Example: you might identify potential software bugs and develop solutions to fix them, or you might create a product roadmap to ensure the product is staying up-to-date with industry trends.
Product and Design Sense: This skill involves understanding the product from a design perspective. It requires the ability to think through how the product looks, feels, and functions from the perspective of the user.
Example: you might design a user interface that is easy to use and visually appealing, or you might develop a product that meets the needs of a specific user group.
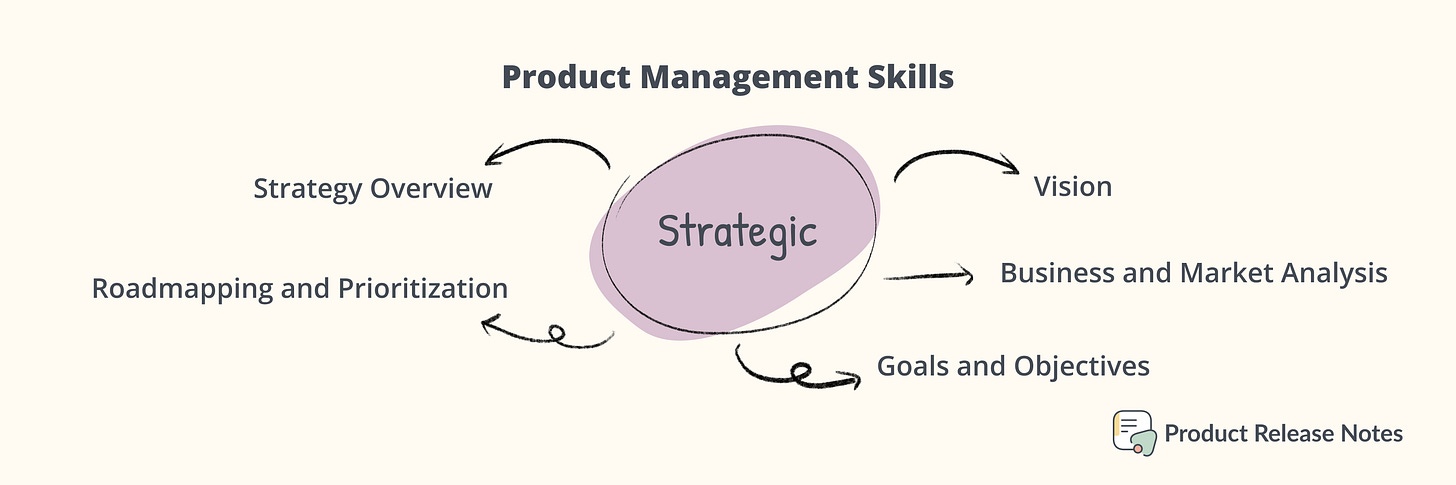
Strategic Skills
Strategy Overview: Product strategy is a plan for developing and launching products and services that meet customer needs and achieve business objectives. It involves an understanding of customer needs, an analysis of the competition, and an assessment of the company's capabilities and resources.
Example: conduct market research, competitor analysis, defining product and service features, and developing pricing models.
Vision: Product vision is a long-term goal for the product that guides product strategy. It should be specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and timely.
Example: create a product roadmap that outlines the steps needed to achieve the vision.
Roadmapping and Prioritization: Roadmapping is the process of creating and communicating the product strategy and vision. It includes creating a timeline for product development, identifying and prioritizing tasks, and creating a budget.
Example: create a timeline for product development activities and prioritize tasks based on their importance.
Business and Market Analysis: It is all about understanding customers, market trends, and competitors. It is used to identify customer needs, market opportunities, and competitive threats.
Example: conduct customer surveys, market research, and competitor analysis.
Goals and Objectives: This is setting measurable goals and objectives for the product and determining how to evaluate progress.
Example: setting short-term and long-term objectives, measuring KPIs, and defining success metrics.
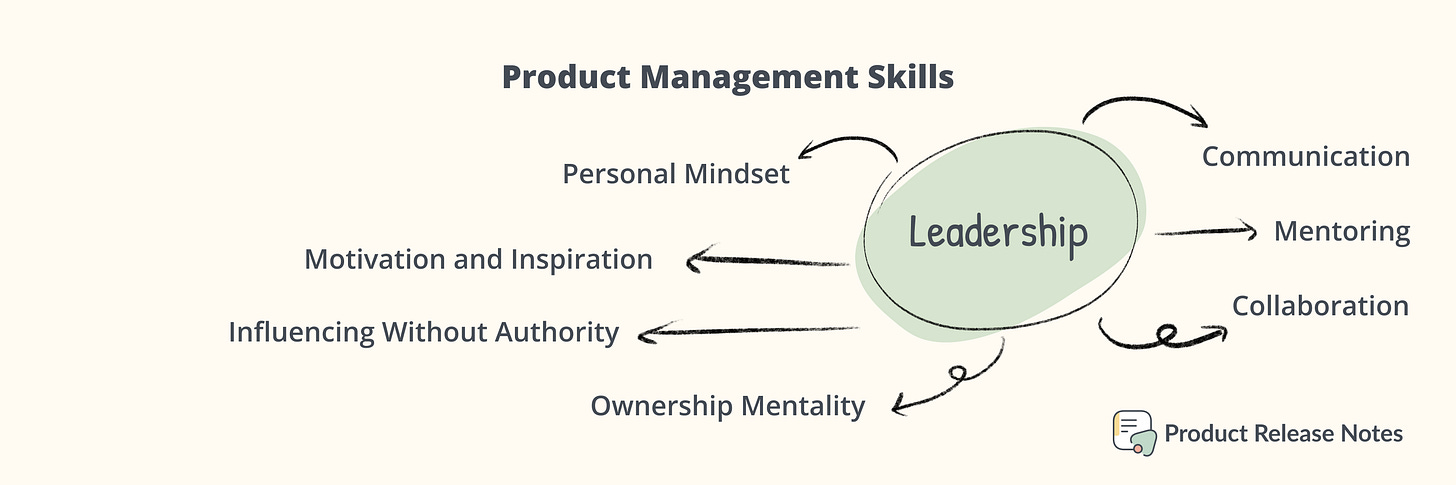
Leadership Skills
Communication: This is the ability a PM use when giving and receiving different kinds of information. Communication skills involve listening, speaking, observing and empathizing. Product management requires good communication skills, because part of their job includes communicating with stakeholders, customers, and team members.
Example: a product manager can use a variety of communication methods to inform stakeholders of the product's progress and get feedback.
Collaboration: Product management requires the ability to collaborate with multiple teams, including engineering, design, marketing, and working with any other departments.
Example: work with the design team to create a user interface that meets the customer's needs.
Personal Mindset: PMs with this skill needs minimal supervision to complete tasks. Attempts to complete tasks independently before asking for help and follows rules/directions as required by the task/situation.
Example: create a list of tasks that need to be accomplished in order to reach the product's goals, know how to ask for help when needed, adapts approach in response to new conditions or others’ actions.
Mentoring: This skill help mentors provide instruction and share their expertise with their mentees. Mentorship involves a two-person partnership with the intention of developing, improving and reaching personal and professional goals.
Example: provide guidance and feedback to team members to help them develop their skills.
Motivation and Inspiration: Product management requires the ability to motivate and inspire team members.
Example: provide incentives and rewards to motivate team members to meet their goals.
Influencing Without Authority: Is the ability to influence others without having any power over them. You don't have to be the CEO, investor, or even the most senior person in the room to have influence. PMs need the ability to influence stakeholders and team members without formal authority.
Example: a product manager can use data and logic to persuade stakeholders to agree with the product's vision.
Ownership Mentality: An ownership mindset means taking responsibility for outcomes and being empowered to make the decisions that will lead to those outcomes. To cultivate an ownership mindset on the team, focus on transparency, autonomy, and customer empathy.
Example: take responsibility for making sure the product is successful and meets customer needs.
People Management Skills
Building a Team: This is a skill that involves creating a team of people who can work together effectively to achieve the desired outcome. This could include selecting the right people for the team, creating team guidelines, organizing team meetings, and providing guidance and support for the team.
Example: create a team of engineers to develop a new product.
Becoming a People Manager: This skill involves taking on the role of managing people. This could include setting goals and objectives, managing performance, providing feedback, and developing strategies to motivate and engage employees.
Example: use a performance management system to ensure employees are meeting their goals and objectives.
Coaching: This skill involves helping employees reach their full potential by providing development opportunities and resources. This could include providing training and mentorship, giving feedback, and offering career guidance.
Example: create a development plan for each employee to help them reach their goals.
People Leadership: is the act of leading relationships in different cultures and environments to create high-performing and collaborative teams that will come together to work as one on a shared goal.
Example: keep PMs accountable, review other’s work, communicate strategy to the team and avoid micromanaging at all cost.
Organizational Excellence: This skill involves creating a culture of excellence within an organization. This could include setting clear expectations, creating systems and processes to ensure quality and consistency, and recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions.
Example: develop a system to track performance and recognize employees who excel.
Do I need all the skills to be a Product Management?
Short answer: No.
Becoming a Product Manager is a multi-faceted process that involves developing the necessary skills and experience, yet it’s not mandatory to learn all of these skills to be a PM. Because different product management roles require different skills depending on their context and the type of product they are managing.
Even if there’s no single set of skills that guarantees to succeed at the job, there’s a bottom line that you can start developing if you want to be a Product Manager. PMs are strategic thinker, they have good communication skills, as well as an understanding of the company’s goals and products. Is also important to understand the market, the customer, and data analysis.
Get the full PM Skills checklist
Here is the freebie I promised to you. This is a PDF version that you can print right away and place it on your desk or wherever it helps to remind yourself the skills you are pursuing this year.
You can use the checklist as you wish. However, here are some examples to help you start with:
Checkmark all the skills you think dominate well, so you can see which ones to focus on next.
Mark with an X those skills you want to improve or focus on this year.
Identify the skills that you know well with a symbol of your preference and mark the other ones you need to improve with a different symbol.






Super useful summary. I’ll use your template to track my progress in some skills this year 👌